In the first six months of the year through June 30, 2017, 29 U.S. entities issued an equivalent number of taxable and tax-free green bonds valued at about $8.0 billion. This is roughly in line with U.S. issuance during the first 6 months of 2016. Worldwide volume, on the other hand, reached $49.1 billion so far this year versus about $37.2 billion last year, or a 32% increase. Based on year-to-date activity, the U.S. represents about 16.3% of global issuance. The pace of issuance during the second quarter, which was fueled by tax-exempt issuers that accounted for 50% of the volume, eclipsed the first three months of the year by a ratio of 2.6X—perhaps signaling the start of a response to the damaging environmental policy initiatives commenced by the present administration in Washington DC. Even with 29 issues hitting the market so far this year, retail investors are still likely to be challenged in efforts to directly invest in green bonds for their portfolios due to competition from institutional investors with their strong demand for green bonds, buy and hold strategies and a continuing demand-supply imbalance. As an alternative, investors can also gain exposure to green bonds through a number of mutual funds and one newly launched ETF.
What are Green Bonds?
Green bonds are equivalent to other fixed income securities, both taxable and tax-free, except that these types of bonds raise funds specifically to finance new and existing projects with environmental benefits that are ultimately geared toward reducing greenhouse gas emissions and limiting the effects of climate change. Green bonds include securities issued by sovereigns, development or supranational banks, corporations, states, cities and local government entities, such as water, sewer or transportation authorities. Green bonds are issued in the form of senior unsecured obligations, project finance or revenue bonds, notes as well as securitizations that collateralize projects or assets whose cash flows provide the first source of repayment. In the future, new green bond structures are likely to be introduced. Also, green bonds, like all other bonds, vary as to credit quality, ranging from investment grade to non-investment grade; and they are issued in varying maturities that can range from the short-to-long term as well as different rates of interest or yields. Importantly, green bonds trade at levels that are equivalent to their non-green counterparts. In other words, investors can support environmental projects with the intent to achieve positive outcomes while at the same time realizing market-based rates of return. Refer to the article entitled Investing in Green Bonds.
Who Issued Tax-Exempt Green Bonds in 1H 2017?
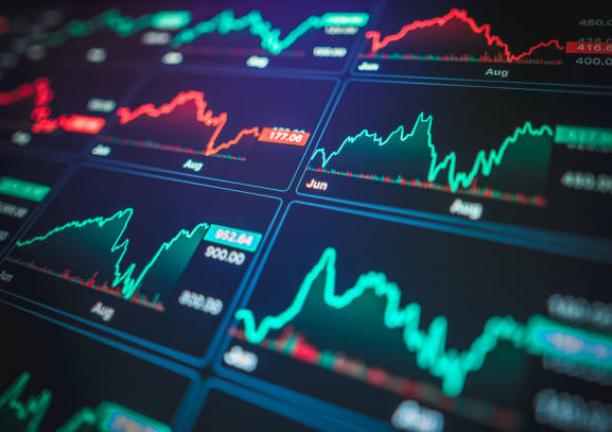
While green bonds were issued by four issuer types during the first six months of the year, the municipal tax-exempt sector led the pack with $4.1 billion in bonds that accounted for 51% of total volume. The second quarter saw an uptick in tax-free issuances that rose from $1.2 billion to almost $3 billion in the second quarter. Corporates, led by Apple Inc. which issued its second green bond in the amount of $1.0 billion, were the next largest but distant second place issuers. Third were securitized transactions, consisting of Property Assessed Clean Energy (PACE) loans and residential solar panel loans, with 4 transactions and almost $800 million. Refer to Exhibit 1.
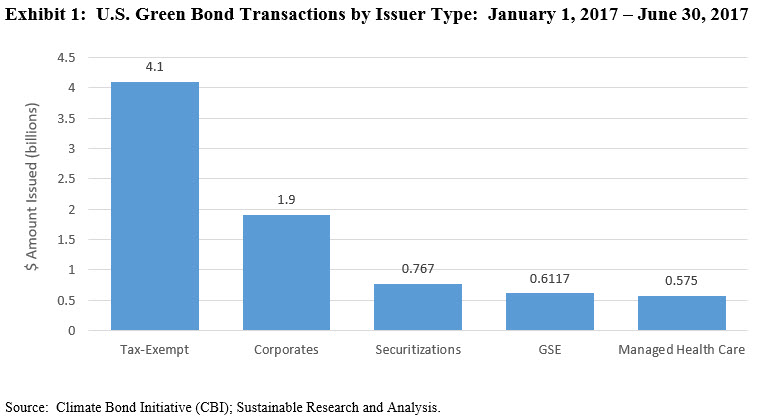
Refer to Appendix 1 at the end of the article for a complete listing of U.S. green bond issuers.
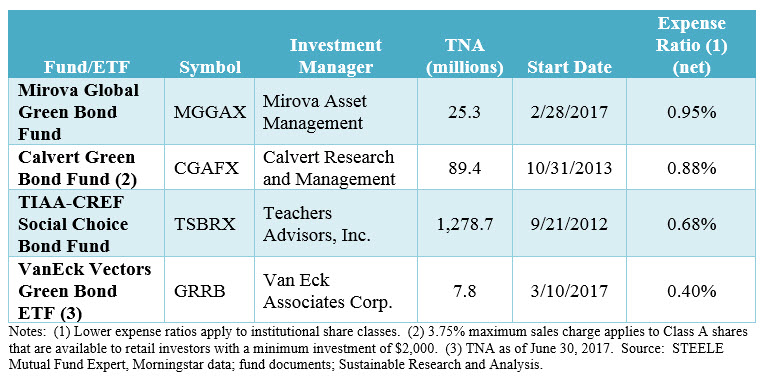
Green Bond Investment Options
Even with 29 issues hitting the market so far this year, retail investors are still likely to be challenged in their efforts to directly invest in green bonds for their portfolios. This is due to competition from institutional investors with their strong appetite for green bonds, buy and hold strategies and a continuing demand-supply imbalance. Oversubscription is common as green bonds tend to be gobbled up by institutional investors. According to some sources green bonds tend to be oversubscribed by 1.5X to 3X the final book. As an alternative, investors can also gain exposure to green bonds through a number of mutual funds and one newly launched ETF. These investment offerings, however, should be evaluated on a case by case basis. See Exhibit 2 for a listing of currently available green bond funds and ETFs. Refer also to article entitled Investing in Green Bonds.
Exhibit 2: Listing of currently available green bond funds and ETFs
Appendix 1: Green Bonds, Type and Dollar Amount Issued: January 1, 2017 – June 30, 2017
(Listed in alphabetical order)